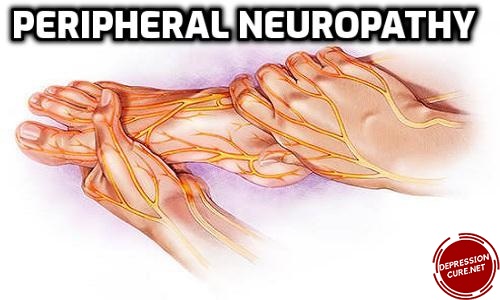
Introduction of Peripheral Neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that affects the regular activity of the nerves of the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is a network of nerves that connects the central nervous system to the rest of the body. Pain in neuropathy can be severe like electric shock.

Nerve damage can result from diseases such as diabetes and treatments such as chemotherapy. The causes of neuropathy can also be genetic. It is most important to determine if neuropathy is the result of a severe underlying problem.
Nerve Conduction Studies, blood tests, MRIs can be used to determine or rule out a possible cause.

Many people suffering from neuropathic pain experience insomnia and depression, and both can increase pain perception. There are several medical treatments your doctor can use to control the condition. The disorder of neuropathy is uncomfortable, but there are treatments available today that can be very useful.
Click Here To Read: Destroy Depression Review – Is It Legit or Scam?
What is Peripheral Neuropathy?

It is a nerve problem that causes numbness and pain, swelling, or muscle weakness in various parts of the body. It generally starts in the hands or feet and gets worse over time. And, it is also called peripheral neuropathy.
Stages of peripheral neuropathy

There are three types of neuropathy:
Neuropathy can affect a nerve. This is called mononeuropathy. Carpal tunnel syndrome is an example of mononeuropathy.
The effect of two or more nerves in different areas is called multiple mononeuropathies.
Many nerves are affected by polyneuropathy.
Most people with neuropathy suffer from polyneuropathy.
Peripheral Neuropathy Symptoms

What are the symptoms of neuropathy?
Each nerve has a specific function in your peripheral system, so symptoms depend on the type of nerves affected. Veins are classified as follows:
Motor nerves that control muscle movement.
Autonomic nerves that control functions such as BP, heart rate, digestion and bladder.
Sensory nerves that receive sensations like temperature, pain, vibration or touch from the skin.

Symptoms of neuropathy are as follows:
Lack of coordination and fall.
Touch sensitivity.
Muscle weakness or paralysis when the motor nerve is affected.
In-sensitiveness in your toes or hands, gradual onset of tremors, which may spread to your feet and arms.
Severe, stinging, cold, or burning pain.
If the autonomic nerve is affected, the following symptoms occur:
- The bladder, digestive or bowel problem.
- Vulnerability to heat and excessive sweating or no sweating.
- Dizziness due to change in blood pressure.
Click Here To Read: 75 Depression Quotes
When to see a doctor?
If you feel unusual prick weakness or pain in your hands or feet, see a doctor immediately. Early testing and treatment can control your symptoms and prevent further damage to your peripheral nerves.
Peripheral Neuropathy Causes and Risk Factors
Why does neuropathy occur?

Peripheral neuropathy occurs when the vein does not function properly due to damage. In neuropathy, the veins do not work correctly – even if there is no pain, the veins can send pain signals, and when you are harmed, the veins may not transmit pain signals.
There are many reasons for neuropathy. The cause may be hereditary or may have developed after birth.
Hereditary Neuropathy

Hereditary neuropathy can affect both motor and sensory nerves. It causes weakness in the leg and lower leg muscles. Deformities in the legs are also common, making it difficult to walk, and you fall as a result. In its later stages, it may also affect the muscles in the hands. There is no cure for hereditary neuropathy.
Acquired Neuropathy
This neuropathy is prevalent. There are several reasons for this, including:
Infections and autoimmune disorders:?
Germs that damage nerve fibers include HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), herpes virus, and the bacteria that cause syphilis. Some autoimmune disorders can also affect nerve tissue. Examples include systemic lupus erythematosus, Guillain-Barr? syndrome, and rheumatoid arthritis.

Systemic diseases:?
Systemic diseases are those that affect the entire body. These include diabetes (which is the leading cause of neuropathy), kidney disease, some cancers, and hormonal imbalances.
Medications and poisons:?
Some medications, including strong drugs (chemotherapy), used to treat cancer, can damage peripheral nerves. Contact with heavy metals (including lead and mercury) and industrial chemicals, especially toxic substances such as solvents, can also affect nerve function.
Click Here To Read: I Love Panic Attacks 100% Genuine Review
Trauma:?
Trauma happens because of sudden injury due to falling, car accident, or playing. Peripheral veins may also be caused by compression of the nerves caused by the narrowing of the traumatic nerves.
Vascular disorder:?
Neuropathy can occur when blood flow to the arms & legs is obstructed by inflammation, blood clots, or other blood vessel disorders. Decreased blood flow deprives nerve cells of oxygen, causing nerve cells to be damaged or destroyed.

The risk of neuropathy is increased due to:
- Being overweight
- High BP
Diabetes:?
If you have diabetes, the risk of nerve damage due to it increases with your age and diabetes.
Excessive alcohol consumption:?
Excessive alcohol consumption can eliminate thiamine and other essential nutrients, which can lead to neuropathy in the arms and legs.
Kidney failure.
Vitamin imbalance:?
Proper intake of vitamins E, B1, B3, B6, B9, and B12 is essential for healthy nerve function.
Be over 40 years old.?
Prevention of Peripheral Neuropathy

How to avoid neuropathy?
If you have a history of this disorder in your family, you can still prevent its onset by doing the following:
- Do regular, moderate exercise
- Avoiding alcohol
- Eat healthy food
- Avoid smoking and quit smoking
You can reduce the risk of neuropathy by:
- Protecting your feet during games, especially in games that use kicking.
- Knowing what toxins you can come in contact with in-office or school.
If you have diabetes:
- Tell your doctor if you experience any symptoms of neuropathy.
- Control your blood glucose levels.
- Get your feet checked at least once a year.
Diagnosis of Peripheral Neuropathy

How is neuropathy tested?
There are many possible causes of neuropathy. In addition to physical tests, which may include blood tests, commonly performed tests.
A complete medical history
The doctor will review your medical history, including your symptoms, your lifestyle, exposure to toxins, drinking habits, and family history of nervous diseases.
Click Here to Read:- 60 Interesting Depression Facts
Neural Tests
The doctor can examine your tendon reflex, your muscle strength and Tightness, your ability to feel the sensation, and your posture and coordination.
The doctor may also ask for the following tests:
Nerve Function Test
Electrocardiography records electrical activity in your muscles to detect nerve damage. The probe sends electrical signals to the nerve, and the electrode placed along the path of the nerve records the nerve’s response to the signal.
Other Nerve Function Tests
They feature an autonomic reflex screen that records how autonomic nerve fibers work, sweat tests, and sensory tests record your ability to feel touch, vibration, coolness, and warmth.
Neural Biopsy
This involves removing a small part of the nerve (usually a sensory nerve) to look for abnormalities.
Skin Biopsy
Doctors remove a small part of the skin to see a reduction at the nerve endings.
Imaging Testing
CT scans or MRI scans can test for herniated discs, tumors, or other abnormalities.
Blood tests
These can detect vitamin deficiency, diabetes, abnormal immune system, and other signs that can lead to neuropathy.
Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment

What is the treatment of neuropathy?
The goal of treatment is to control the condition caused by neuropathy and relieve symptoms. If the tests do not indicate an underlying condition, doctors carefully wait to see if your neuropathy improves.
Click Here To Read: 10 Ways To Be A Good Mother
The medicines
Apart from the medicines used to treat the conditions of neuropathy, the medications taken to relieve the symptoms of neuropathy are as follows:
Painkiller
Over-the-counter medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, may help relieve mild symptoms. For more severe symptoms, doctors may also prescribe painkillers (pen-killers).
Anti-Caesar Medications
Medications such as gabapentin and pregabalin, developed to treat epilepsy, can relieve nerve pain. Side effects include sleepiness and dizziness.
Topical Treatment
Capsaicin cream, which contains the substance found in cayenne pepper, may moderately improve symptoms of neuropathy. When you apply these creams, there may be irritation on your skin, but it usually subsides over time.
However, some people cannot afford it.
Lidocaine (local anesthetic) patch is another treatment that you can get rid of the pain by applying on your skin.
Antidepressant
Some tricyclic antidepressants, such as Amitriptyline, Doxepin, and Nortriptyline, can help relieve pain by interfering with chemical processes (which make you feel pain) in your brain and spinal cord.
Therapy
Various treatments and procedures can help reduce symptoms of neuropathy.
Physiotherapy
If your muscles are weak, then physiotherapy can help improve your function. You may also need arm or leg braces, a stick, a walker, or a wheelchair.?
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
Electrodes applied to the skin provide electric current at different frequencies. This should be done daily for 30 minutes a month.
Plasma exchange and intravenous immune globulin
Plasma exchange involves removing your blood, then removing antibodies & other proteins from the blood, then returning the blood to your body. In immune globulin therapy, you receive a good amount of proteins that act as antibodies (immunoglobulins).
Surgery
If you have neuropathy due to pressure on the nerves, such as pressure from a tumor, you may need surgery to reduce the pressure.
Click Here To Read: 15 Insomnia Facts
What are the complications of Peripheral Neuropathy?
Infection
Your feet and other organs lacking sensation can be injured without you knowing. Check these areas regularly & treat minor injuries before they become infected, especially when you have diabetes.
Burns and Skin Trauma
You may not feel temperature changes or pain in parts of your body (which are numb).
Falling
Weakness and inability to feel can be associated with a lack of balance and falling.
Note: Depression Cure does not provide any type of medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.