What is Parkinson disease?
Parkinson disease is a fast-spreading disorder of the nervous system that affects your movements. It develops slowly. The disease sometimes starts with tremors occurring in only one hand.
However, when tremor becomes the most prominent sign of Parkinson disease, the disorder also causes stiffness or slow movements.
In the early stage of Parkinson’s disease, your facial expressions may decrease or disappear, or your arms may stop moving while walking.
Your voice may be slow or unclear. Symptoms become severe as Parkinson disease increases over time.
The causes of Parkinson’s disease are not known and require much research. Parkinson disease cannot be cured, but medications can improve your symptoms.
In some cases, physicians may suggest surgery to settle certain areas of your brain and improve symptoms.
Parkinson disease Symptoms
What are the signs & symptoms of Parkinson disease?

The symptoms & signs of this disease may vary from person to person. Early signs may be less and do not easily attract anyone’s attention. Its symptoms often start appearing on one side of your body, and the condition becomes very bad. After this, the whole body starts getting affected by the symptoms.
Click Here To Read: Destroy Depression Review – Is It Legit or Scam?
Signs and symptoms of Parkinson disease may include –

Tremor
Shivering or shaking usually starts with your hands or fingers. This can cause your thumb and index finger to start rubbing against each other, which is called “Pill-Rolling Tremor.” A symptom of Parkinson disease is a shiver in your hand in a relaxed state.
Slow activity (Bradykinesia)?
Over time, the disease can reduce your ability to move and function, which makes it easier to perform an easy task and takes longer. You may slow down while walking or have difficulty in standing. Also, you try to drag by dragging your feet, which makes it difficult to walk.
Stiff muscles
Muscle stiffness can occur in any part of your body. Stiff muscles can limit your movement and cause pain.
Impaired Posture and Imbalance
Parkinson’s disease can result in your body bowing or imbalance.
Loss of spontaneous movements
In Parkinson’s disease, there may be a decrease in the ability to perform unconscious tasks, including blinking eyelids, smiling, or shaking hands. While talking, your face may not have a long gesture.

Changes in voice
Parkinson’s disease can result in pronunciation problems. Your tone may be slow, loud, and fuzzy, or you may hesitate before talking. Your voice gets worse than a typical infection. Vocal and language therapists can help troubleshoot your pronunciation problems.
Changes in handwriting
The handwriting may be small, and there may be difficulty in writing.
Medications can alleviate many of these symptoms. See the “Treatment” section below for more information.
When to see a doctor?
If you notice any symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease, contact your doctor. Also, consult a doctor to test your condition and rule out other causes of symptoms.?
Click Here To Read: What Ended The Great Depression
Parkinson disease Causes & Risk Factors
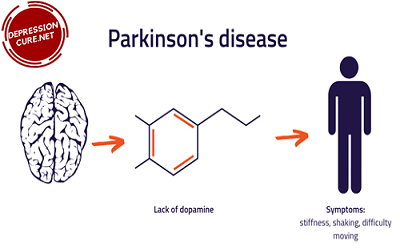
Causes of Parkinson’s disease:
In Parkinson’s disease, some nerve cells (i.e., neurons) present in the brain slowly degenerate or perish. Neurons produce a chemical called dopamine in our brain.
Many symptoms arise due to the destruction of these neurons. The subsequent decrease in dopamine levels causes abnormal brain activity, resulting in signs of Parkinson disease.
The cause of Parkinson disease is unknown, but there may be various factors that cause it to occur.
Your Genes
Researchers have identified specific genetic mutations that can cause Parkinson disease. However, these are uncommon except in rare cases involving family members affected by Parkinson disease.

Environmental Causes
Effects of certain toxins or environmental factors may increase the risk of end-stage Parkinson disease, but overall they reduce Parkinson disease risk.
In summary, more research is still needed to identify the factors responsible for Parkinson disease.
What are the risk factors for Parkinson’s disease?

Risk factors for Parkinson disease include the following:
Growing age
Parkinson disease is very rare in young people. It usually begins in the middle or last phase of life, and the risk increases with age. The disease usually develops in people 60 years of age or older.
Heredity
You are more likely to develop this disease because of a close relative of Parkinson. However, as long as some members of your family do not get the disease, your risk is low.
Men are on high Risk
Men are more likely to develop Parkinson disease than women.
Exposure to Toxic Substances
Continuous exposure to herbicides and pesticides may increase your risk of developing Parkinson disease slightly.
Click Here To Read: 25 Ways To Simplify Your Life
Prevention of Parkinson Disease
How can I prevent Parkinson disease?
Since the cause of Parkinson disease is unknown, the methods of its prevention are also a mystery. However, some reports and research have shown that caffeine found in coffee, tea, and Coca-Cola may reduce the risk of developing Parkinson disease. Green tea can also help reduce their risk.
Some research and report have shown that regular aerobic exercise can reduce the risk of the disease.
Diagnosis of Parkinson disease
How is Parkinson disease diagnosed/ tested?
There is currently no specific test for Parkinson disease. Trained physicians (neurologists) in nervous system conditions will diagnose the disease based on the patient’s medical history, a review of the patient’s signs & symptoms, and a neurological and physical examination.
At the same time, your doctor may suggest tests to rule out other conditions that may be the cause of your symptoms.
In addition to testing, doctors can give you Parkinson disease drug ‘carbidopa-levodopa.’ If there is a significant improvement from taking this medicine, then it is often considered to be confirmed by Parkinson disease.
Adequate doses should be given to see the effect of the drug, as lower doses for one or two days are not beneficial. For the best response, the medicine should be taken on an empty stomach at least one hour before meals.
Sometimes, it takes a long time to diagnose this disease. The doctor may suggest you have regular checkups with trained neurologists to periodically evaluate your condition and symptoms and diagnose the disease.
Parkinson Disease Treatment
What is the treatment of Parkinson disease?
Parkinson’s disease cannot be cured, but medications can help control your symptoms. In some severe cases, surgery may be advised.
Your doctor may also recommend lifestyle changes, especially by adding aerobic exercise. In some cases, physical therapy is also very important. It emphasizes balance and stretching.
-
Medicines
Medications can help relieve problems related to your gait, activity, and vibrations by increasing the supply of dopamine in your brain. However, dopamine cannot be given directly, as it cannot enter your brain.
Your symptoms may improve significantly after treatment of Parkinson disease begins. Over time, the effect of medications often diminishes, although symptoms can usually be controlled fairly well.
Your doctor may prescribe the following medicines:
Carbidopa-Levodopa
Levodopa is the most effective drug for Parkinson’s disease. It is a natural chemical that goes into your brain & is converted into dopamine. This medicine may have some side effects like dizziness or nausea (orthostatic hypotension).
After several years, when your disease increases, the effect of levodopa medicine may not remain stable and may be reduced or increased.?
Also, you may experience involuntary movements (dyskinesia) after taking an overdose of levodopa. Your doctor may reduce the dose of your medicine or regulate the time of taking the medication to control these effects.
Dopamine Agonists
Agonists produce dopamine-like effects in the brain. They are not as effective as levodopa in treating symptoms of Parkinson disease. However, their effects last longer and can be used in conjunction with levodopa to reduce the greater effects of levodopa.?
Some of the side effects of dopamine agonists are similar to levodopa, but they also include hallucinations, bloating, drowsiness, and repetitive behaviors – such as gambling.
MAO-B inhibitors
These help prevent brain dopamine damage by inhibiting a brain enzyme called monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). This enzyme divides the brain dopamine into small segments.?
Side effects may include headaches or nausea. Taking these drugs with levodopa increases the risk of hallucinations in the patient. These drugs are generally not used in combination with antidepressants or certain types of neurotics due to severe but rare effects.?
Contact your doctor before taking any additional medications with MAO-B inhibitors.
Click Here To Read: 40 Interesting Phobia Facts
Catechol O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors
This drug increases the effect of levodopa therapy by inhibiting the enzyme that breaks down dopamine. The side effects include the risk of involuntary activities (dyskinesia), which is mainly aggravated by the effects of high doses of levodopa. Other side effects include diarrhea or side effects resulting from an overdose of levodopa.
Anticholinergics
These drugs have been used for many years to control the tremor associated with Parkinson disease.?
However, the minor benefits of these drugs often have no effect on side effects, such as memory loss, confusion, hallucinations, constipation, dryness in the mouth, and difficulty in passing urine.
Amantadine
Doctors may suggest amantadine to provide short-term relief from symptoms of early-stage Parkinson disease. It may also be given with levodopa therapy in later stages of Parkinson disease to control involuntary activities (dyskinesia) induced by carbidopa-levodopa. Side effects may include a purple spot on the skin, swelling of the ankle, or hallucinations.
-
Surgical Procedures
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
Surgeons implant electrodes into a specific part of your brain. The electrodes are connected to a generator implanted in the chest near your collarbone. These send electrical vibrations to your brain and can reduce the symptoms of Parkinson disease.
Risks associated with surgery include infection, brain hemorrhage, or stroke. Some people experience problems related to the DBS system or experience complications due to exacerbations. Your doctor may need to replace or adjust parts of the system concerned.
Deep DBS is mostly used for people with high stage Parkinson disease who have unstable reactions to the drug levodopa.
DBS can continuously improve symptoms of Parkinson disease, and they persist for many years after the correction process. However, DBS cannot completely prevent Parkinson disease from growing.
Parkinson disease Complications
What other Problems can cause Parkinson disease?
Parkinson disease sometimes occurs with the following additional problems that can be treated:
Difficulty in Thinking
You may experience cognitive problems (dementia) and difficulty thinking. This usually occurs in the later stages of Parkinson disease. Such cognitive problems do not show a more positive response to medications.
Depression and Emotional Changes
A person with Parkinson disease may have depression. You may also experience other emotional changes, such as anxiety, fear, or lack of motivation. Doctors can give you medicines to treat these symptoms.
Swallowing problems
As your condition progresses, you may have problems with swallowing. This is not a severe problem in specific Parkinson disease. Slow swallowing can cause saliva to accumulate in your mouth and drip out of the mouth.
Sleep problems
People with Parkinson disease often have sleep problems, such as sleeplessness overnight, waking up early, or sleeping during the day.
Bladder related problems
Bladder problems can occur in this disease, including the inability to control urine or pain or discomfort in urinating.
Constipation
Many people with Parkinson disease become constipated, mainly due to the slow functioning of the digestive system.
Click Here To Read: 50 Interesting Sleep Facts
You can also experience:
Changes in blood pressure
When you stand up due to a sudden decrease in blood pressure (orthostatic hypotension), you may feel dizzy or weak.
Trouble smelling
You may experience trouble associated with olfaction. You may have difficulty identifying an odor or knowing the difference between more than one odors.
Fatigue
Many people suffering from this disease lack energy and feel tired. The reason for this is not always known.
Pain
In this disease, many people have pain either in specific parts of the body or in the whole body.
Sexual dysfunction
Some people suffering from this disease often have low libido.
Note: Depression Cure does not provide any type of medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.